In this article, you will see a detailed review of the computer virus types that are currently active. Malware is ranked by the hazard level. And remember – there is no harmless malware!
There are dozens of computer virus types and subtypes, and even more of them if we mention the currently unused malware types. “Market environment” in the cybercriminal world changes extremely quickly, so the things that are actual today may be useless next week. But there are still enough “players” who keep going for a decade or even more without any problems. Let’s check the most popular (and sustainable!) ones.
What is a computer virus and types of virus?
First of all, it is important to make several remarks about the post theme. Computer virus, exactly, is an umbrella term for all types of malicious software. However, it is a misleading term – the virus is just a separate type of malware. It was designed to infect the files with its own code – and force these files to replicate the virus, again and again – just like a biological virus does. Calling all malware “viruses” refers to the early-mid ‘00s when viruses were really one of the most widespread types of malware. Then, this word became a common noun – just like kevlar for aramid fiber or xerox for a copying machine.
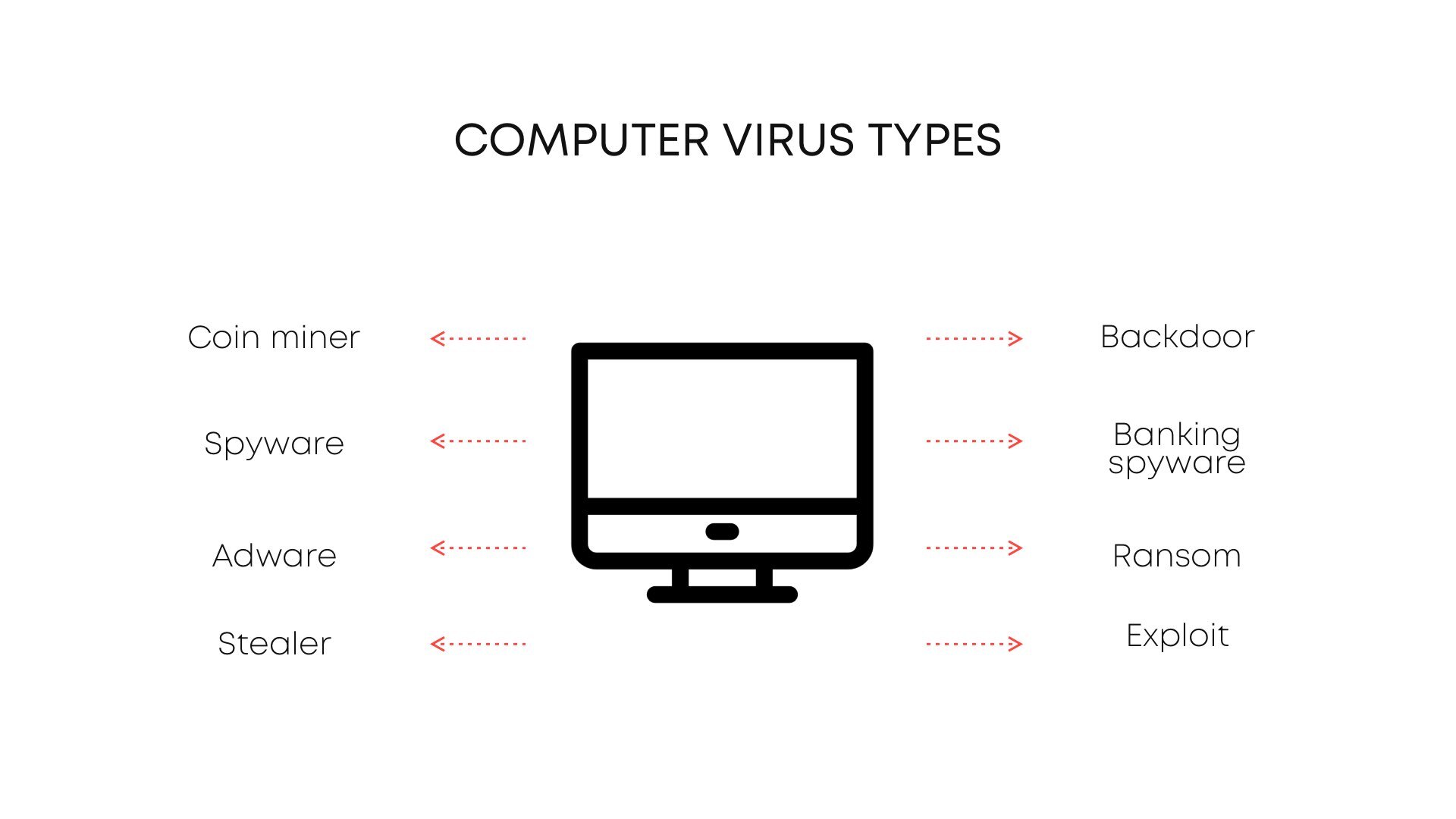
Types of viruses are, exactly, the separated classes of ones, that distinguish from each other by their functions, purposes and damage level. Some of the viruses that are used actively nowadays are just intermediary malware. They are injected just to inject more viruses shortly after – and to make your computer much more vulnerable to attacks. Those are exploits and downloaders. But let’s check all things one-by-one – sorted by widespread.
Adware
Adware is a type of malicious software that controls the functionality of websites of any kind and offers additional advertisements. Ads tend to decrease the page-load speed and loading speed of the sites. Besides, ads inject lots of JavaScripts – and this process degrades the performance of your computer. Moreover, this thing is extremely exploitable – so don’t be surprised to see a lot of other viruses on your PC.

Adware is, however, not a problem for most online stores or e-commerce places, including Facebook, Google, eBay, Amazon and Yahoo, and many others, that offer lots of online services for free. But this is not the case for internet advertising that is placed away from specialized sites. The services offered by adware are popular among the same non-legit advertisers, but who cares if everyone gets its profit?
Browser hijackers
Brother-in-arms of adware, this computer virus type takes control of your web browser. It changes your search engine, redirects all your queries through it (even if you open Google, your query will be redirected to Bing, for example) and shows you the ads you can’t get rid of. It may be a separate program, a little inject into your browser configurations, or – the most popular thing nowadays – the browser plugin. Browser hijackers can block you the access to browser settings – hence, you will not be able to change the settings after malware activity.

What is coin miner virus?
A “cryptocurrency miner” virus, or simply a coin miner, is a malicious program that exploits your hardware without your permission. These viruses utilize special cryptographic algorithms to calculate the transaction hash. The most popular cryptocurrencies that are mined by fraudsters are Monero and DarkCoin. These bad guys usually embed their coin-miner virus in shady downloading pages or inside of the strange banner that is shown to you by adware. There are also rare cases when coin miners are spread as browser plugins.
The main danger of coin miners is that they can increase your hardware wear significantly. While regular gaming or 3D modeling creates a portioned load that does not last on the peak rates for a long time, cryptomining takes as much as possible during the whole process. It makes your hardware overheated, wears your heat sinks, and what is more critical – your GPU.
Spyware and stealers
I decided to group these viruses, since they are very similar. Both of them are used in attacks against individuals as well as against companies. And both of these computer virus types are actively used by some governments – to spy on unreliable citizens, for example. Most of the “massive” spyware and stealers make money on selling the stolen data to third parties – advertising agencies or cybercriminals.
Why are these categories interested in what spyware steals? These viruses take everything they can reach, starting from your PC configuration and up to your conversations. They can also manage to steal some of your files – and these docs can contain something pretty valuable. That’s why, exactly, stealers are more often used as “aimed” malware. Spyware is effective when a massive strike is needed – for example, to steal hundreds of accounts and start posting spam from them.
Downloader viruses and exploits
Downloader viruses act exactly as their name means. They prepare your system to malware injection – disable your security tools, UAC and other system protection features. Then, downloaders inject the so-called payload – a pack of various viruses that will completely wreck your PC. Which viruses will be in the payload – only the God knows, but you would not be happy to observe what happened to your computer. Downloader viruses are pretty popular nowadays for commencing attacks on corporations.
Exploit malware acts for the same purpose – to weaken the target system and to inject additional malware. However, the exact way of how does it reach its target is different. While downloader just bans the anti-malware software and opens all network connections, exploit malware searches for possible vulnerabilities in the software. And the possible effects of exploit activity (i.e. the damage of malware that the exploit downloaded) are much wider.
What is ransomware?
So, here is the most dangerous thing you can currently meet in the Internet. Ransomware is designed for money extortion. You can call its appearance by downloading the hacked programs or by browsing dubious sites. It tries to take away your files and your data. The goal is to make you pay in order to get access to it. The type of criminals behind this kind of virus is the same that operates in all viruses – they are called ransomware operators.
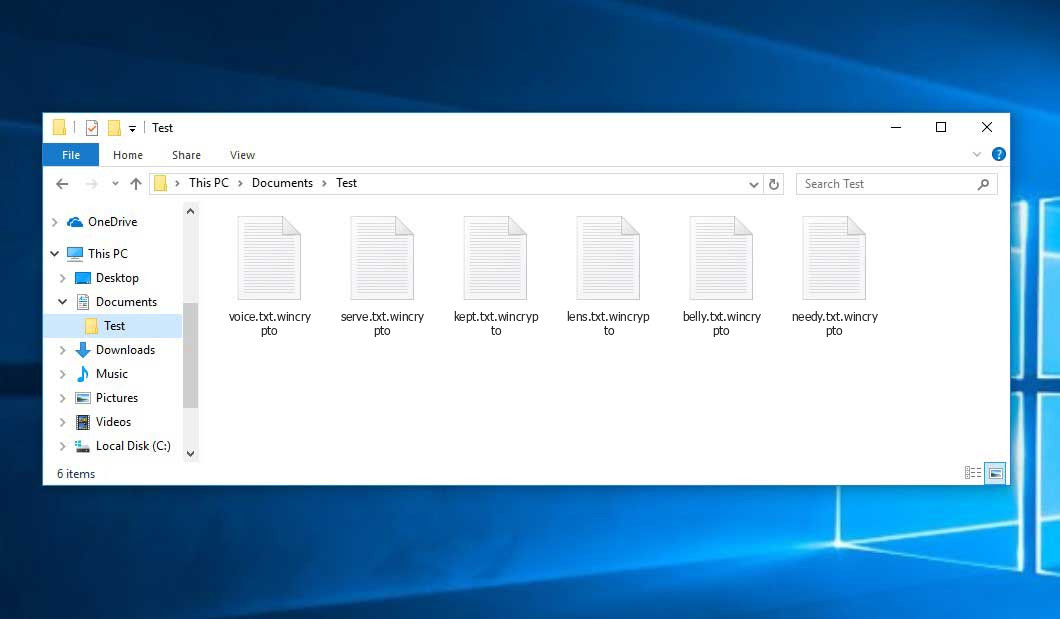
Even if these files are usually encrypted – you need to pay and unlock your system in order to get it back. However, the very first thing you need to do is to identify this type of virus. Some of the ransomware families – such as HiddenTear, for example – are flawed by design. That allows the victims to decrypt their data without any payments – just by using the free decryptor. Even if the files are not decryptable – it is important to know your enemy’s face.
What is a backdoor virus?
A backdoor is a special type of malware that gives access to a system in such a way that no one else can get it. Usually, it uses some of the system elements to provide itself a sustainable position in your Windows. It can perform many tasks such as injecting malicious code to a computer system, or capturing everything the computer can see. It usually manages to avoid detection by antivirus programs, to take complete control over your system – and sometimes, to read its data. The most common purpose of a backdoor is the creation of botnets. Rarely, they act as downloaders – but with the ability of a remote access tool.





