Xiaomi Smartphones with MediaTek Chips Are Vulnerable to Counterfeit Payments
Analysts have identified problems in the payment system that are present on Xiaomi smartphones with MediaTek chips, and which provide a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) responsible for signing transactions.
These bugs can be used to sign fake payment packages using a non-privileged third party application. Among the consequences of such an attack can be both disabling the mobile payment mechanism and forgery of transactions (signing transactions from the user’s mobile wallet to the attacker’s wallet).Let me remind you that we also wrote that Information security experts suspect Chinese company Xiaomi of spying on users, and also that Lithuanian authorities discovered censorship in Xiaomi smartphones.
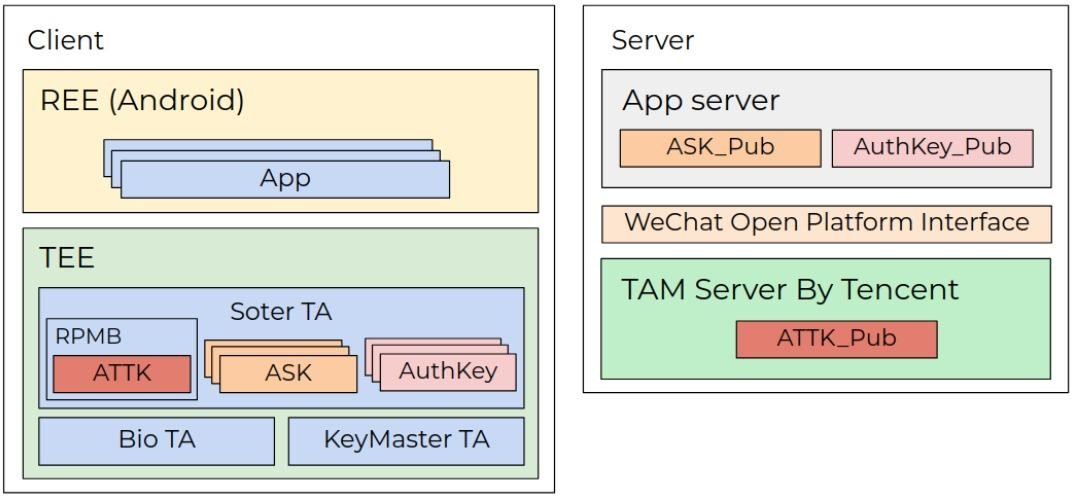
Check Point experts explain that Xiaomi smartphones with MediaTek chips use the Kinibi TEE architecture, which has a separate virtual enclave to store the keys needed to sign transactions. This space is designed to run trusted applications such as thhadmin, which is responsible for managing security, including the built-in Tencent Soter mobile payment platform and providing an API for integrating payment capabilities.
That is, applications such as WeChat Pay and Alipay, which together have over a billion users, rely on the Tencent Soter API to verify payment packages and complete transactions.
As the researchers found out, in the trusted application format that Xiaomi uses, a bug was found related to the lack of version control. This problem opens the door to a downgrade attack, meaning a hacker can replace a newer and more secure application with an older and more vulnerable version. As a result, the researchers bypassed the Xiaomi and MediaTek patches by overwriting the thhadmin application in MIUI 12.5.6.0 with the application from MIUI 10.4.1.0, which opened up many opportunities for subsequent abuse.
Experts were also able to exploit another vulnerability (CVE-2020-14125) in the trusted Tencent Soter application, which allows an attacker to extract private keys and sign fake payment packages in the context of an unprivileged user.
For users of vulnerable Xiaomi smartphones, a patch is already available – the June security updates for Android, which fix the CVE-2020-14125 vulnerability.
However, the downgrade vulnerability is a third-party issue, and so far, Xiaomi representatives have only confirmed that a fix is being worked on and should be released in the near future.





