Russian Hackers Launched a Massive Spear-Phishing Campaign
In mid-January 2022, Mandiant specialists discovered a spear-phishing campaign launched by the Russian group APT29, and now Russian hackers have moved on to large-scale attacks.
The attack targeted diplomats and government organizations. The group previously worked alongside APT28, participated in the hacking of the Democratic National Committee, and it was in a spate of attacks targeting the 2016 US presidential election.Let me remind you that we also wrote that 14,000 Gmail users were notified of APT28 attacks. We also reported that Due of the sanctions, Russian hackers are looking for new ways to launder money.
In a recent hacking campaign uncovered by Mandiant, phishing messages sent from hacked email accounts of embassies of different countries became the attack tool. Government employees used Atlassian Trello, DropBox and cloud services as part of their C&C infrastructure.
Experts observed several waves of attacks between January 2022 and March 2022.
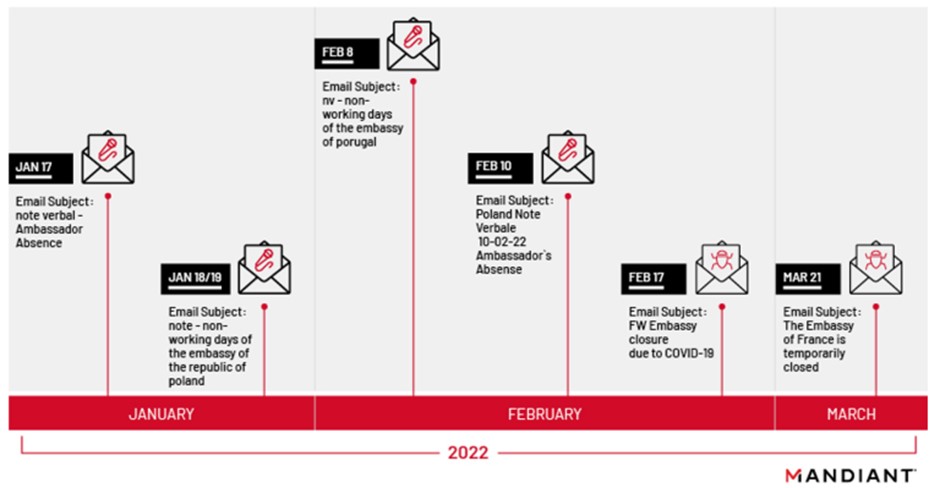
Timeline of the 2022 phishing campaign
After opening the file attached to the letter, ROOTSAW writes data to disk in IMG or ISO format. The image contains a Windows shortcut (LNK) and a malicious DLL. Clicking on an LNK file executes a malicious DLL. To trick the victim into running the file, attackers use a fake icon.
After the DLL is executed, the BEATDROP loader is delivered to memory and starts operation.
Experts also reported that APT29 has replaced BEATDROP with BEACON. The new bootloader is based on Cobalt Strike and implements backdoor features, including keyboard recording, screenshots, collecting and extracting various data, port scanning and much more.
Having gained a foothold in the desired network, the grouping quickly tries to elevate privileges. Sometimes hackers were able to gain domain administrator rights in less than 12 hours after a phishing attack.
Once they gain access, the attackers conduct extensive reconnaissance of nodes and the active directory environment. APT29 has also been seen conducting reconnaissance on hosts to gather credentials.





