First ransomware exploiting Log4Shell problem discovered
Experts warn that attacks on the vulnerability in the Log4j library are increasing: now the specialists of the Bitdefender company have discovered the Khonsari ransomware exploiting a fresh bug called Log4Shell.
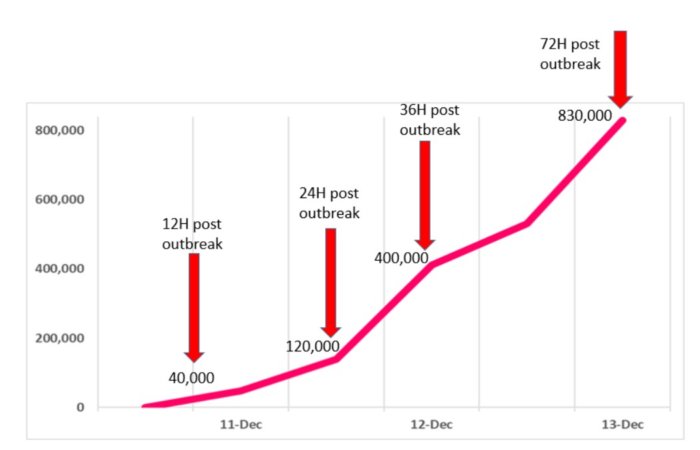
The first attacks on Log4Shell were recorded shortly after the vulnerability was publicly disclosed. However, then it was about the introduction of miners, DDoS malware, theft of environment variables and the installation of Cobalt Strike beacons (for unclear purposes).However, the attacks are intensifying. Thus, according to Check Point, more than 60 exploits for Log4Shell have already been studied, and at some moments can be observed up to 100 attacks per minute. As of the beginning of the week, since last Friday, various hacker groups have already carried out about 840,000 attacks on Log4Shell.
In turn, the Chinese company Qihoo 360 warned that it is already tracking at least 10 different hack groups that abuse the vulnerability.
Now Bitdefender analysts have reported that they discovered the first group of ransomware to abuse the new vulnerability. The first attacks by the new Khonsari ransomware were noticed on Sunday, December 11, 2021. The malware is known to be written in .NET and is intended only for attacks on Windows machines. Victims can recognize the Khonsari attack by the .khonsari extension, which the malware adds to most encrypted files.
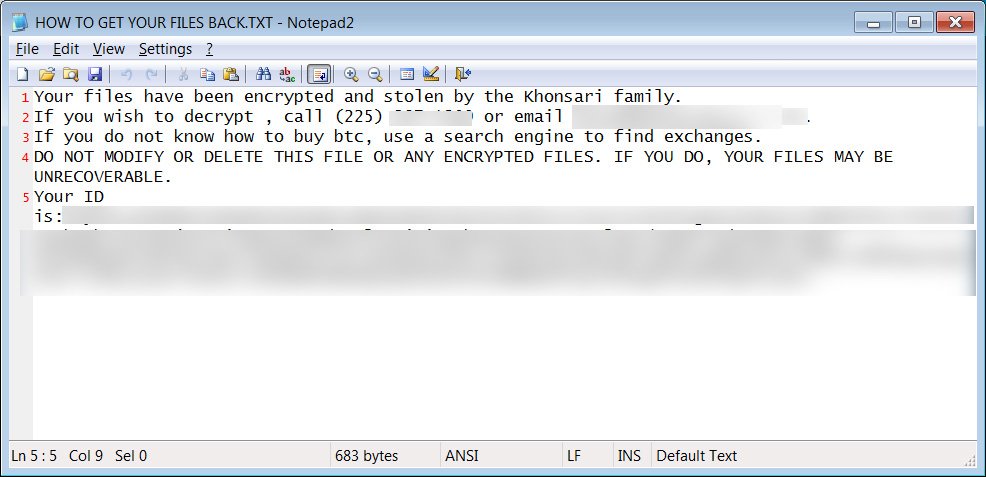
Khonsari extortionate note. Photo credit: Bleeping Computer
The ransomware was also noticed by MalwareHunterTeam and information security expert Michael Gillespie, who describe the threat as skidware that does not require special skills and is based on low quality publicly available sources. Despite this, they admit that the ransomware works and is able to encrypt the system after a successful attack on Log4Shell.
Even worse, it is reported that the ransomware uses a very strong encryption method, and so far no flaws have been found in it, that is, after encrypting the files, victims will either have to restore data from their backups or pay the attackers.
However, it is not known whether the victims will have the opportunity to pay the ransom. The researchers noticed that the malware is named after a real person (the owner of an antique shop in Louisiana) and uses his contact details in ransom notes. It is not yet clear who this person is, and why hackers denigrate his name in such a strange way. However, apparently, Khonsari may turn out to be someone’s cruel joke and a wiper. That is, it will be impossible to recover data after an attack.
Let me remind you that we talked about the fact that Chinese APTs are interested in Log4Shell vulnerability.





