Mirai Botnet Comes with new 11 Exploits to Attack Enterprise Devices
For the first time, the activity of this version of Mirai was recorded in January 2019. Up to this point, the botnet attacked routers, surveillance cameras, modems and controllers.
Now the vulnerable presenters of WePresent WiPG-1000 and LG Supersign TVs installed in corporations have been added to this list.
Moreover, the attackers added 11 new exploits to 16 existing ones. Thus, the total number of exploits has reached 27. Previously, the Palo Alto Networks team discovered that the malicious component is stored on a Colombian company server.
According to the statement, this server “provides electronic security systems, integration and monitoring alarms”.
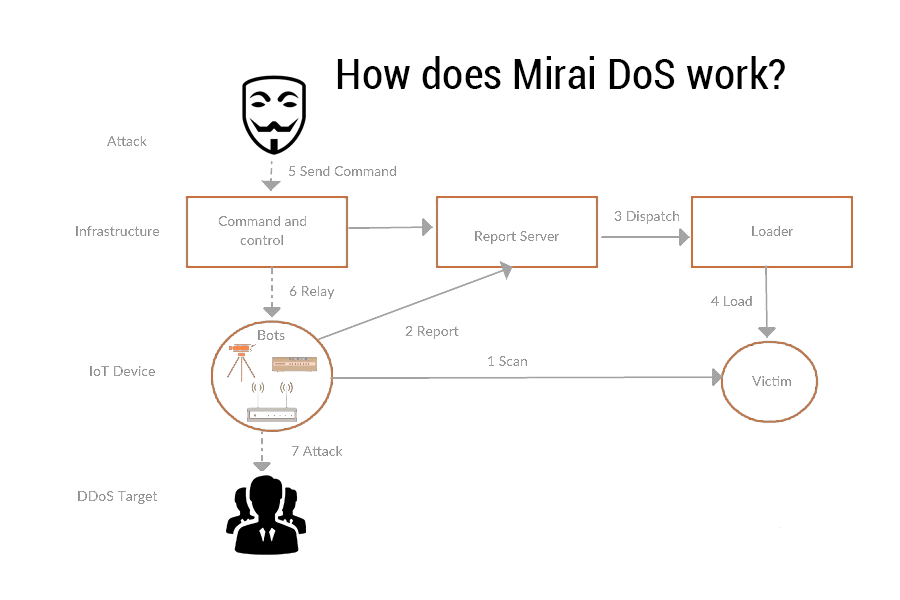
What is Mirai malware?
Mirai is a malware that infected Linux IoT devices or gadgets in August 2016. The attack remained in the type of a botnet that createdan enormous DDOS storm. An example, targets included Italian political websites , Minecraft servers, and Russian auction. The DDoS had secondary results on other very big service providers that used their services such as Sony PlayStation servers, Amazon, GitHub, Netflix, PayPal, Reddit, and Twitter. In total 600,000 IoT devices were infected as part of the botnet cumulative.
The new Mirai variant spotted by Unit 42 also comes with a handful of new features:
1. It makes use of the same encryption scheme as is characteristic of Mirai with a table key of 0xbeafdead.
2. When decrypting strings using this key, we found certain unusual default credentials for brute force that we haven’t come across until now.
3. It uses the domain epicrustserver.cf at port 23823 is for C2 communication.
4. In addition to scanning for other vulnerable devices, the new version can be commanded to send out HTTP Flood DDoS attacks.
“These new features afford the botnet a large attack surface. In particular, targeting enterprise links also grants it access to larger bandwidth, ultimately resulting in greater firepower for the botnet for DDoS attacks,” according to Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42
| Vulnerability | Affected Devices |
| CVE-2018-17173 | LG Supersign TV |
| WePresent WiPG-1000 Command Injection | WePresent WiPG-1000 Wireless Presentation systems |
| DLink DCS-930L Remote Command Execution | DLink DCS-930L Network Video Cameras |
| DLink diagnostic.php Command Execution | Routers DLink DIR-645, DIR-815 |
| Zyxel P660HN Remote Command Execution | Routers Zyxel P660HN-T |
| CVE-2016-1555 | Netgear WG102, WG103, WN604, WNDAP350, WNDAP360, WNAP320, WNAP210, WNDAP660, WNDAP620 |
| CVE-2017-6077, CVE-2017-6334 | Netgear DGN2200 N300 Wireless ADSL2+ |
Denial-of-Service (DoS)
Denial-of-service(Dos) attack is a malicious attempt to make a server or network resources unavailable to users, usually by temporarily interrupting or suspending the services of a host connected to the Internet. DoS attack causes the system to crash or unable to respond in time to make the site unavailable to users. The most popular type of DoS attack occurs when a hacker “floods” the system by overloading the system with “useless traffic” so a user is prevented from accessing their e-mail, website, etc.