FinCEN Tied $ 5.2 Billion Transactions to Ransomware Operations
The Financial Crimes Investigation Unit under the US Treasury Department, also known as FinCEN, reported about $ 5.2 billion in ransomware transactions in cryptocurrency.
FinCEN representatives write that this number was obtained after analyzing 2,184 suspicious activity reports filed by US financial institutions over the past decade (from January 1, 2011 to June 30, 2021). While the reports initially identified $ 1.56 billion in suspicious activity, a subsequent study of the ten most common ransomware programs found additional transactions worth about $ 5.2 billion, attributable exclusively to these hack groups.
In total, FinCEN experts identified 177 CVC (“Convertible Virtual Currency”) wallet addresses that were used for payments related to encryptors.
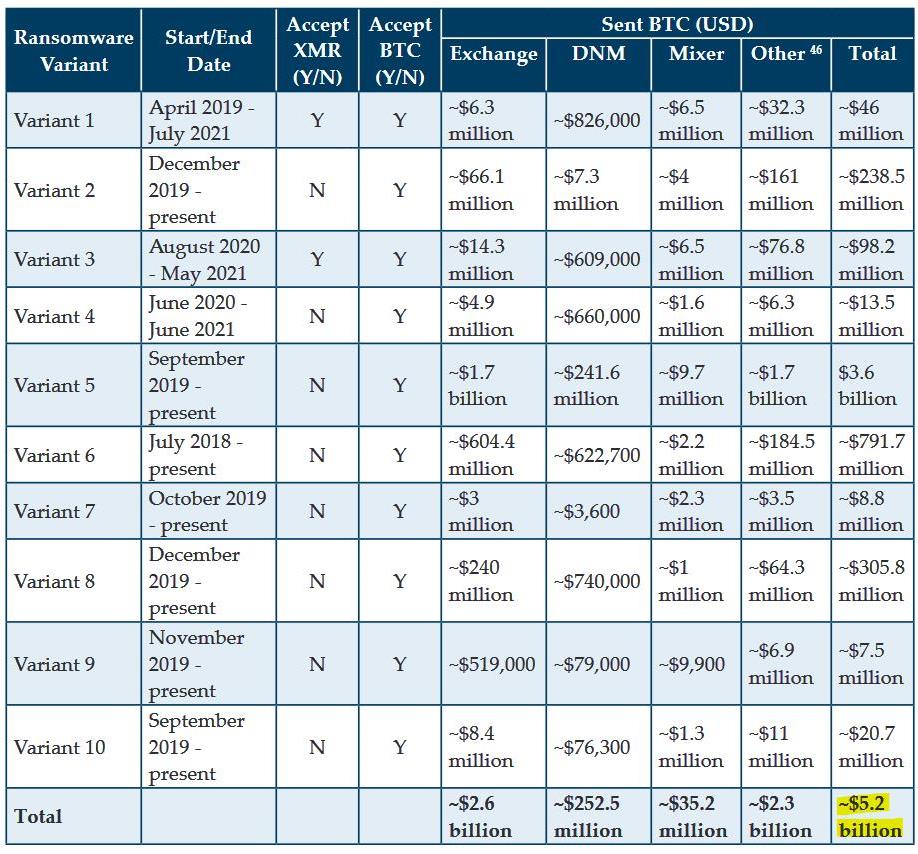
Although the FinCEN report also contains data on fairly old attacks, most of the investigation focused on the first half of 2021 and analysis of the latest trends. The results of this analysis are the following:
- in the first half of 2021, financial institutions filed 635 reports of strange activity related to suspected ransomware activities;
- reports mention 458 suspicious transactions worth $ 590 million;
- the indicators for the first half of 2021 exceed the indicators for the entire 2020 as a whole, which clearly indicates an increase in the activity of ransomware;
- average monthly ransomware transactions in 2021 totalled $ 102.3 million, as
FinCEN detected 68 different variants of such malware active in the first half of 2021; - in the first half of 2021, the most common malware samples were REvil / Sodinokibi, Conti, DarkSide, Avaddon, and Phobos.
Also, FinCEN analysts note several trends in the field of money laundering operations using ransomware. Among them:
- using anonymous cryptocurrencies such as Monero;
- refusal to reuse wallets so that information security companies cannot identify and track transactions;
- using the chain hopping technique to exchange funds for other cryptocurrencies;
- cashing out funds on centralized exchanges;
- use of mixing services and decentralized exchanges to convert revenue.
Let me remind you that we also talked about the fact that The US government has warned agencies about cybersecurity risks for years.