- In 2002, the American teenager Zhislen Raza for fun shot a video in which he portrayed the hero of the film “Star Wars”, using a baseball bat instead of a lightsaber. His classmates, without asking permission, posted a video on the Internet, where the recording was viewed by millions of people. A special website was set up two years later with it and derived from it rolls, special effects and music from the film, which grossed more than 76 million visitors. Videos featuring Zhislen became the most downloaded file 2004 year. The label “Child Star Wars» (Star Wars Kid) is so changed his attitude in the school, that parents were forced to go to a psychiatrist, as well as to
- Classmates 15-year-old Judy Rumb created a website dedicated to its excessive weight and the date of the coming death.
- Kyle Kenny was forced to change schools several times due to a site “Corporation” Kill Kylie “, on which its coordinates were made public along with incriminating information; in the end she was forced to go on home schooling.
- 16-year-old Jed Presto did not leave the house and tried to commit suicide after a dispute with the guys from his school. They began to terrorize the teenage night calls, spreading rumors on the Internet, send insulting sms-messages.
- 13-year-old Ryan Patrick Galagan killed himself, unable to withstand the attacks of former friends, the purpose of which was to prove that the man – gay. After the death of her son’s father found the correspondence with the girl, who met with Ryan, but broke off relations with him and released his private letters. “Tomorrow I will do that, read in the newspaper” – Ryan wrote to those who hunted him, and they said: “This is a fun game!”.
This is a rough list of the most rules that can help parents protect children from the negative impact of the Internet.
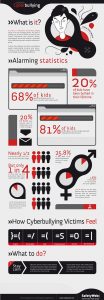
Adults are little thought about the dangers of cyber-wide practice of their children, although the consequences of bullying real hears often: reports of injuries inflicted by peers, attempted suicides and tragic death. Unfortunately, these cases are often accompanied by adult helplessness: “I cannot imagine how this could happen,” “This was a good boy…” The traditional bureaucratic system to silence the problem, search the target of false accusations and to the absence of an adequate response to such incidents lead to the fact that even the real bullying, we do not know enough. A cyber-bullying is invisible, and the damage caused to them – unrecognized. But it is quite realistic, despite the virtuality of this problem.
Cyber-bullying involves a whole range of behavior, at the minimum end of which – a joke that is not taken seriously in the same radical – Virtual psychological terror that causes irreparable harm, leading to suicide and death. There is also the concept of bullitsida – the death of the victim as a result of bullying.
US researchers have identified eight main types of bullying:
- Sparring, or flaming – exchange of short emotional cues between two or more people, usually takes place in a public place the web. Sometimes it turns into a protracted conflict. At first sight, flaming – the struggle between equals, but under certain conditions, it can turn into an unequal psychological terror. The unexpected attack can cause the victim severe emotional distress.
- The attack, permanent debilitating attack (harassment) – repeated offensive messages directed at the victim (for example, hundreds of SMS on mobile phones, regular phone calls) with an overload of personal communication channels. There are also chat rooms and forums, online games are using this technology griefers (grieffers) most often – a group of players, with the aim of not winning, and the destruction of the gaming experience of other participants.
- Slander (denigration) – dissemination of false information and insulting. Text messages, photos, songs, which are often sexual in nature. The victims are not only some teenagers – sometimes happen mailing lists (“who’s who in the school”, “who is sleeping with whom”), created a special “book for criticism» (slam books) with jokes about classmates.
- Imposture, the reincarnation of a certain person (impersonation) – the pursuer has positioned itself as a victim, using her password to access the account in social networks, blog, email, instant messaging, or create an account with your nickname and the same exercise on behalf of the victims of the negative communication. The organization “wave feedback” occurs when the victim’s address without her knowledge sending provocative letters to friends.
- Sell, extortion of confidential information and its dissemination (outing & trickery) – for personal information and its publication on the Internet or transfer those to whom it was not intended.
- Alienation (ostracism, isolation). Any person is inherent desire to be included in the group. Exclusion from the group is perceived as a social death. The more a person is excluded from the interaction, the worse he felt, and the more his self-esteem drops. In a virtual environment, this can lead to complete destruction of emotional child. Online alienation possible in all types of environments where password protection, create a list of spam or a friend. Cyber-stigma manifests itself in the absence of reply to instant messages or emails.
- Сyberbullying – the hidden victims of stalking in order to organize attacks, beatings, rape, etc.
- Heppisleping (Happy Slapping – slamming happy, joyful beating) – the name comes from the English cases in the subway, where teens beat passers-by, while others recorded it on a cell phone camera. Now this name stuck for any video recording of the actual scenes of violence. These videos posted on the Internet, where they can be viewed by thousands of people, without the victim’s consent. Starting out as a joke, heppisleping can end in tragedy: 18 years Tristona Christmas beaten by a group of guys taking it on video for the Internet, and when he was dying on the floor of the header, the killer and the observers continued to have fun at the party.
Here are a few tips that should give the child to overcome this problem:
- Do not rush to throw out your negative into cyberspace. Let the child consults with adults, before responding to the aggressive message. Older children offer rules: before you write and send messages, you must calm down, appease the anger, resentment, anger.
- Create your own online reputation, do not buy into the illusion of anonymity. While cyberspace and provides additional opportunities to feel the freedom and looseness due to the anonymity, the child must know that there are ways to find out who is behind a particular nickname. And if incorrect actions in the virtual space lead to real harm, all the secret becomes clear. Internet history records, which is composed of members of public action and determines each online reputation – gained the image of the person in the eyes of the other participants. The tarnish that reputation is easy to fix – it’s hard.
- Keep the confirmation of the facts of the attacks. If the child is very upset message, image, video, etc., should immediately seek the advice of parents and older children – to save or print the page on their own, to consult with adults at a convenient time.
- Ignore the negative identity. Disposable abusive posts best ignored – often cyber-bullying as a result of this behavior is stopped at an early stage. Experienced participants in online discussions follow the rule: “The best way to deal with inadequate – ignore.”
- If you witnessed cyber-bullying, the correct behavior will be: a) to oppose the aggressor, to make him understand that his actions are evaluated negatively, and b) support the victim – in person or in a public virtual space to give her emotional support) to tell an adult the fact of improper behavior in cyberspace.
- Blocks the aggressors. The instant messaging programs have the ability to block messages from specific addresses. Pause in communication often discourages aggressors desire to continue the persecution.
- Do not ignore aggressive messages if you send letters to an unknown systematically contain threats or pornographic scenes. In this case, you must copy the messages and seek to law enforcement agencies. If offensive information is available on the website, you should make a request to the administrator to delete it.
Completely eradicate cyber-bullying, as well as other manifestations of violence in the virtual space and the real world, it is impossible. But this does not mean that adults can ignore this phenomenon, suspended from the protection of their children and the regulation of adolescent conflicts. Adults should keep aware of the problem of school teachers – this will allow them to more closely monitor conflicts in real life, the combination of which with cyber-bullying is a particularly dangerous. In some cases it is necessary to talk with a psychologist.