Remove TG33 Virus (.TG33 Files Ransomware) – Matrix Ransomware
TG33 Virus Ransomware
The TG33 stands for a ransomware-type infection. The virus comes from the Matrix ransomware family. TG33 was elaborated specifically to encrypt all major file types. As soon as the file is encrypted people are not able to use them. TG33 adds the “.TG33” extension for each file encrypted by it. For example, the file “myphoto.jpg“, once encrypted by TG33, will be renamed into “myphoto.jpg.TG33“. As soon as the encryption is completed, TG33 places a special text file into every folder containing the encrypted data.The message given by TG33 text file requesting the ransom is definitely the like the statements given by other ransomware representatives belonging to the Matrix clan. It actually discusses that the information is encrypted and that the only way to restore it is to use a a special decryption key. Regretfully, this is absolutely true. The sort of cryptography mechanism used by TG33 is still not properly examined. Still, it is definitely particular that each victim might be given the specific decryption key, which is absolutely unique. It is impossible to restore the files without the key available.
Another trick of TG33 is that the victims cannot get to the key. The key is saved on a specific server run by the frauds related to TG33 ransomware. To get the key and recover the important info people have to pay the ransom.
TG33 encrypted your documents, but that might not be the only damage done to you. The ransomware might still be hidingon your computer. To identify whether this holds true, we suggest downloading GridinSoft Anti-Malware.
Download GridinSoft Anti-Malware
GridinSoft Anti-Malware Review, How to get free trial?, EULA, and Privacy Policy.
Nonetheless, irrespective of the asked for quantity, people need to stay away from paying the virus. Cyber frauds are not fair, so they tend to totally disregard what their victims feel about the issue, even when the payment reaches their pockets. This is why paying the ransom typically does not provide any positive outcome and people simply waste their money for nothing.
We highly recommend that you do not contact these crooks and definitely do not transfer money into their accounts. It is said to admit that there are no utilities able to crack TG33 ransomware and to recover the information data totally free. Hence, the only best decision is to recover the lost data from the available backup.
Virus Summary
| Name | TG33 Ransomware |
| File Extension | .TG33 |
| Type | Ransomware |
| Family | Matrix |
| Short Description | The ransomware encrypts all the data stored on your system and requires a ransom to be paid on your part supposedly to recover your important files. |
| Symptoms | File encryption by the ransomware is performed by means of the AES and RSA encryption algorithms. Once the encryption is completed, the ransomware adds its special TG33 extension to all the files modified by it. |
| Distribution Method | Spam Emails, Email Attachments |
| Similar Infections | Fg69, J91d, Bg85 |
| Removal Tool | GridinSoft Anti-Malware |
Keep in mind that the web is now overwhelmed with threats that look similar to TG33 ransomware. It is similar Fg69 and many other ransomware-type threats. Malicious programs of such kind are normally elaborated to encrypt important information and to state the demand before the user to pay the ransom. The peculiarity of all such ransomware threats is that all apply a comparable algorithm to create the special decryption key for data decryption.
Therefore, as long as the ransomware is still being developed or has some hidden bugs, manually recovering the information is simply not feasible. The only method to avoid the loss of your important information is to frequently create backups of your important information.
Bear in mind that even if you create such backups, they should be placed into a special storage utility not connect to your main computer. You may use the USB Flash Drive or external hard disk drive for this purpose, or refer to the help of the cloud storage. If you store your backup files on your common system they may be encrypted together with other files, so it’s certainly not a good storage location.
How did ransomware infect my computer?
There are a number of ways used by online scams to distribute TG33 ransomware. Although it is uncertain how exactly TG33 injects your PC, there are some leaks through which it may penetrate the system:
- integration with third-party software application, especially freeware;
- spam e-mails from unidentified senders;
- websites rendering free hosting services;
- pirated peer-to-peer (P2P) downloads.
Often TG33 ransomware might exist as some legitimate software application, for example, in the pop-ups instructing users to implement some important software application updates. This is the typical trick used by online scams to persuade people into downloading and installing TG33 infection manually, by ways of their direct participation in the installation process.
Furthermore, the criminals may refer to various email spam techniques to inject malicious codes into Windows PC. So, they may describe to sending unsolicited spam e-mails with tricky notifications promoting users to download the attachments or click on certain download links, for example, the ones motivating users to open some video, documents, tax reports or invoices.
Needless to mention, opening such documents or clicking on such dangerous links may seriously harm the PC. Fictitious Adobe Flash Player upgrade notifies may result in TG33 ransom injection. As for the cracked software, these illegally downloaded programs may likewise contain malicious codes leading to TG33 secret installation. Finally, injection of TG33 may happen by ways of Trojans that secretly get injected into the system and set up malicious utilities without the user’s permission.
Is there any way to prevent the injection of TG33 ransomware?
Although there is no 100% guarantee to avoid your system from getting infected, there are some pieces of suggestions we want to show with you. First of all, be very mindful when you browse the web and specifically while downloading totally free programs. Keep away from opening suspicious email attachments, especially when the sender of the email is not familiar to you.
Bear in mind that some freeware installers may consist of other unwanted utilities in the package, so they may be harmful. Make certain that your current anti-virus and your entire OS is always appropriately updated.
Obviously, downloading pirated software is prohibited and may lead to vital damage to be made for your PC. Hence, stay away from downloading cracked software. You are likewise highly advised to reconsider your existing security software and possibly change to another security solution that can render much better services of defending your Windows.
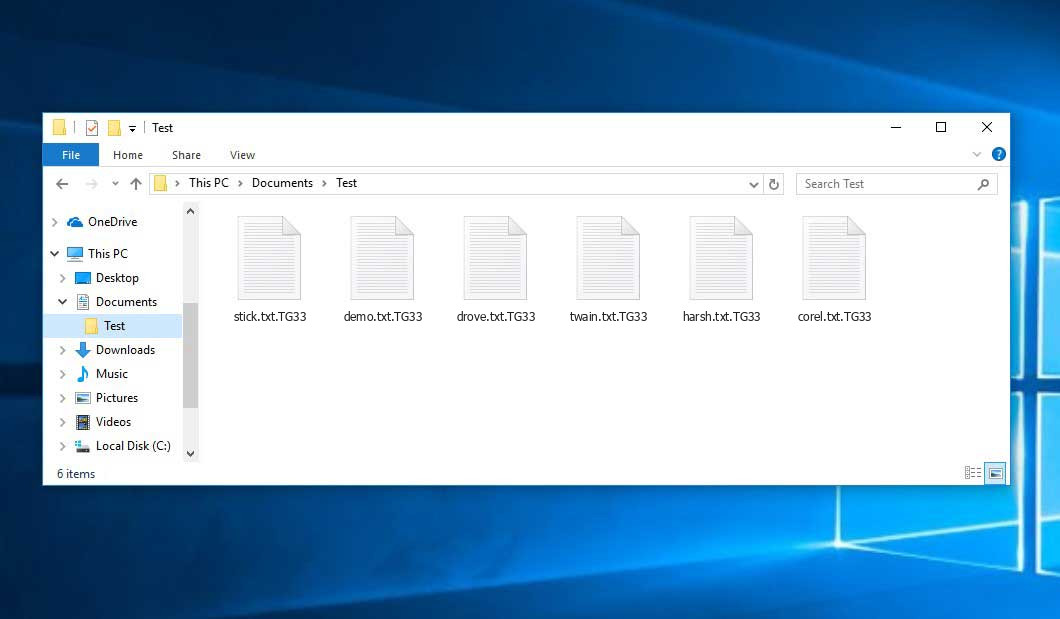
Screenshot of files with “.TG33” extension added by the ransomware:
Use GridinSoft Anti-Malware to remove TG33 ransomware from your computer
1.Download GridinSoft Anti-Malware.
You can download GridinSoft Anti-Malware by clicking the button below:
2. Double-click on the setup file.
When setup file has finished downloading, double-click on the setup-antimalware-ag.exe file to install GridinSoft Anti-Malware on your computer.
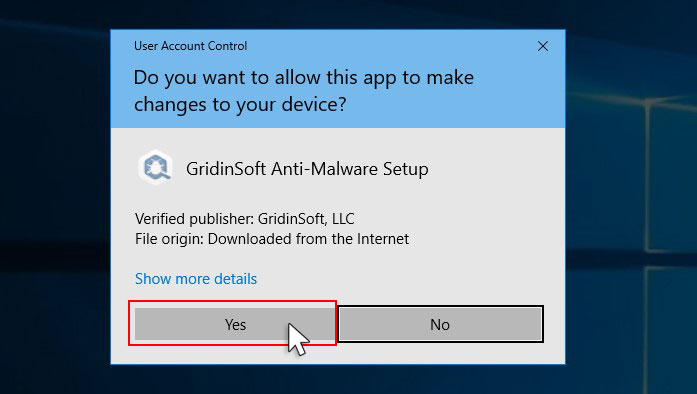
An User Account Control asking you about to allow GridinSoft Anti-Malware to make changes to your device. So, you should click “Yes” to continue with the installation.
3. Press Install button for run GridinSoft Anti-Malware.
3.Once installed, GridinSoft Anti-Malware will automatically run.
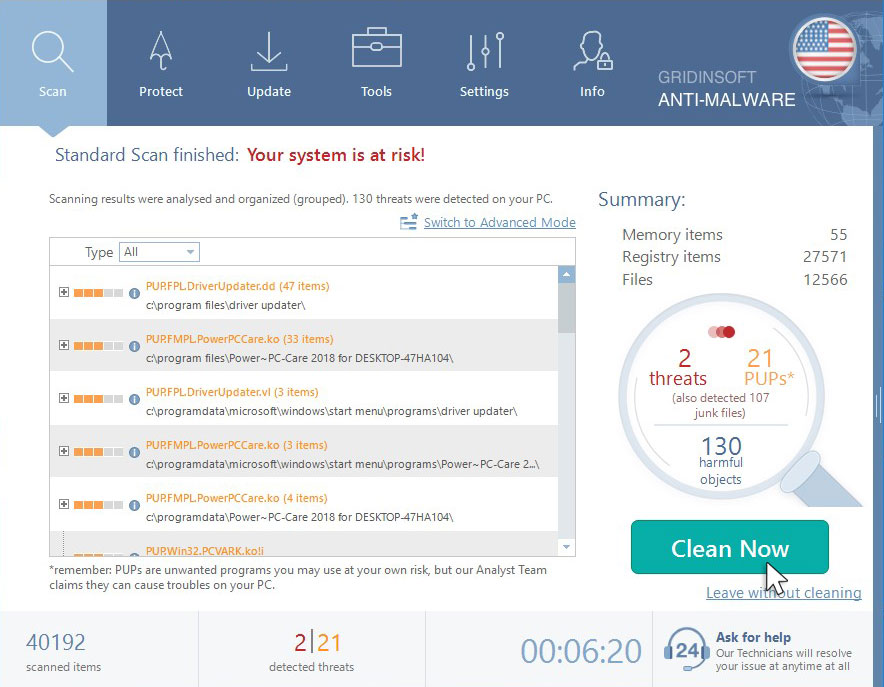
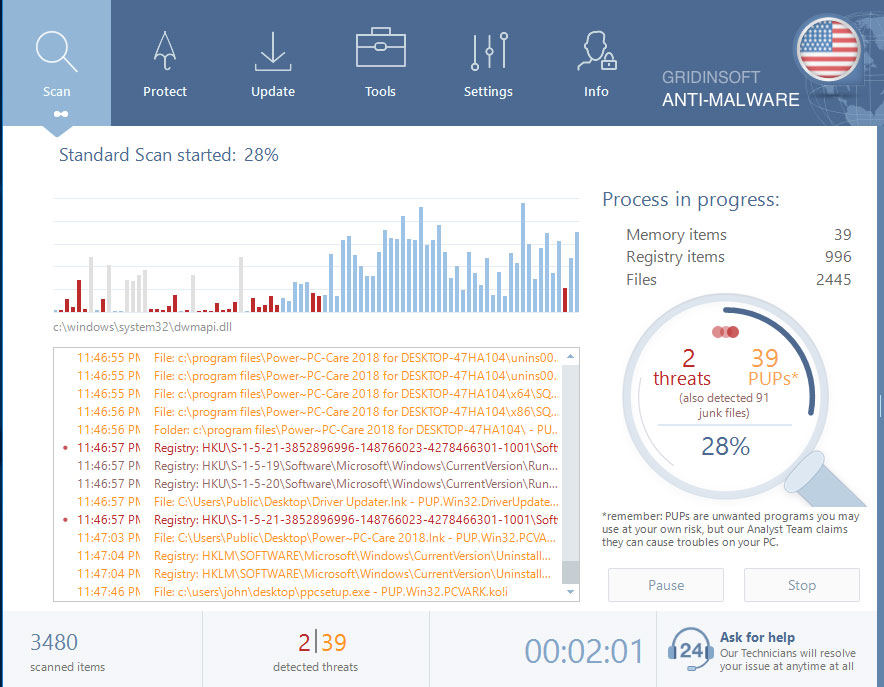
4. Wait for the GridinSoft Anti-Malware scan to complete.
GridinSoft Anti-Malware will automatically start scanning your computer for Win Speedup 2018 and other malicious programs. This process can take a 20-30 minutes, so we suggest you periodically check on the status of the scan process.
5. Click on “Clean Now”.
When the scan has completed, you will see the list of infections that GridinSoft Anti-Malware has detected. To remove them click on the “Clean Now” button in right corner.